In the vast field of materials science, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), with its unique properties and broad application potential, has emerged as a high - performance elastomer material that garners significant attention. From daily necessities to high - end industrial products, TPU has demonstrated irreplaceable value.
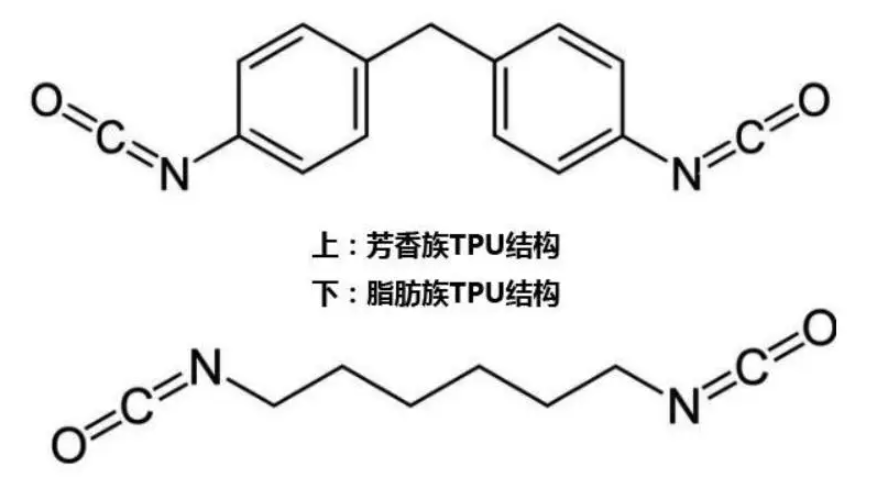
TPU, or Thermoplastic Polyurethane, is a block copolymer composed of soft segments and hard segments. The soft segments are generally made up of polyols, endowing the material with elasticity and flexibility. The hard segments are generated by the reaction of isocyanates and chain extenders, providing strength and rigidity. The variety of types and ratios of soft and hard segments gives TPU diverse properties.
The main synthesis methods are bulk polymerization and solution polymerization. Bulk polymerization can be further divided into the prepolymer method, where diisocyanate reacts with macroglycol first, and then a chain extender is added to produce TPU; the one - step method involves simultaneously mixing macroglycol, diisocyanate, and a chain extender for the reaction. In solution polymerization, diisocyanate is first dissolved in a solvent, then macroglycol is added for a reaction, and finally, a chain extender is added to produce TPU.

Wide Hardness Range: With a Shore hardness ranging from Shore A 60 to Shore D 80, the hardness can be adjusted by changing the ratio of soft and hard segments. Even when the hardness changes, it still maintains good elasticity and wear resistance.
High Mechanical Strength: It has outstanding load - bearing, impact - resistance, and shock - absorption properties. The tensile strength can reach 35 - 50MPa, the elongation at break exceeds 600%, the resilience is excellent, and the compression set is low (less than 30%).
Good Wear Resistance: The Akron abrasion loss is less than 40mm3, which is about 5 times more wear - resistant than ordinary rubber.
Excellent Flex Resistance: Under the action of repeated periodic stress in different environments, it can still maintain excellent flex resistance characteristics.
Wide Temperature Adaptability: It can operate within a temperature range of - 40℃ to 120℃ and can withstand 150℃ for a short time. It has good flexibility at low temperatures and is not easy to crack.
Good Air Tightness: It can be easily welded by high - frequency or heat - pressing, making it suitable for inflatable products. The air tightness of polyester - based products is better than that of polyether - based products.
Oil and Chemical Resistance: TPU is a highly polar polymer material with low affinity for non - polar mineral oils. It is hardly eroded in various oils, and polyester - based types have even better oil resistance. It also has resistance to many chemical substances.
Hydrolysis Resistance: It has good water resistance under turbid conditions. Polyether - based types will not show obvious hydrolysis within 1 - 2 years. Polyester - based types will decompose when soaked in water at specific temperatures for a certain period.
High - Temperature and Oxidation Resistance: It has good antioxidant ability and can withstand temperatures up to 120℃. Compared with some plastic raw materials, it is more stable at high temperatures.
Biomedical Properties: It has good biocompatibility, being non - toxic, non - allergenic, and free from local irritation and pyrogenicity.
Good Processability: It can be processed using methods suitable for thermoplastic materials such as injection molding, extrusion, calendering, and blow molding. It can also be made into polymer alloys with complementary properties with certain polymer materials.
Environmentally Friendly and Recyclable: It does not require vulcanization, has a short production cycle, and waste materials can be recycled. It complies with environmental protection standards such as EU REACH and RoHS.
It can be divided into polyester - type, polyether - type, and butadiene - type, containing ester groups, ether groups, or butenyl groups respectively.
It can be divided into urethane - type and urethane - urea - type, obtained from diol or diamine chain extenders.
It can be divided into pure thermoplastic (pure linear structure without cross - links) and semi - thermoplastic (containing a small amount of cross - links such as urethane carbamate).
It can be divided into special - shaped parts (mechanical parts), pipes (sheaths, rod - shaped materials), films (thin sheets, plates), as well as adhesives, coatings, and fibers.
It is used for soles and uppers, providing elasticity, wear resistance, and comfort. It is also used to make waterproof and breathable films, sports protective gear, etc. For example, the midsole of Adidas Boost technology sports shoes uses TPU to achieve energy return.
It is used to manufacture mobile phone cases and smartwatch straps, with impact resistance and scratch resistance. Headphone wires have high resilience and are anti - tangling.
Automotive wire harness sheaths are oil - resistant and aging - resistant. Interior skins and air ducts have a soft touch and strong weather resistance.
It is used for medical catheters, tourniquets, etc., meeting biocompatibility requirements.
It is used for seals, hydraulic hoses, etc., with high - pressure resistance and chemical corrosion resistance.
High - fluidity TPU filaments are used for customized insoles, flexible robot components, etc.
With its unique molecular structure, excellent performance characteristics, diverse classification methods, and wide application fields, TPU occupies an important position in modern material applications. With the continuous progress of science and technology, TPU materials are expected to be expanded and applied in more emerging fields, continuously bringing new surprises and changes to people's lives and industrial production.



