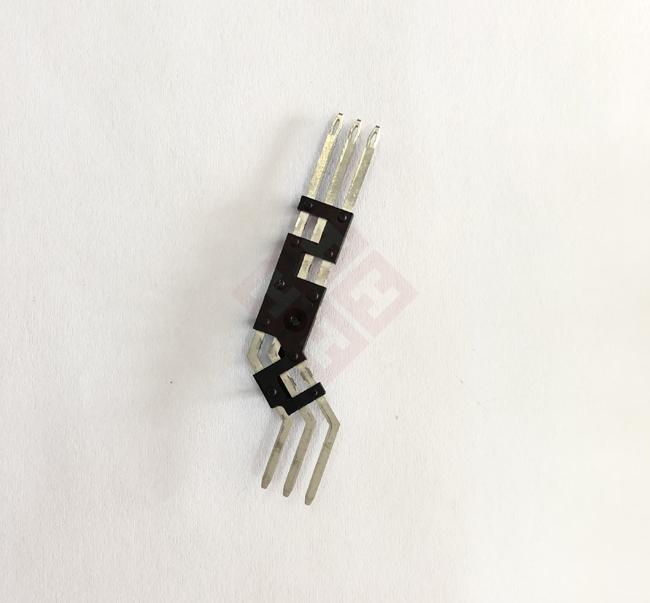
Automotive pin socket injection molds are key tools used to manufacture the pin sockets in automotive connectors.
I. Design Key Points
Material Selection
Plastic Materials: Select engineering plastics such as PBT, PA6T, and LCP to meet the requirements of electrical insulation, high-temperature resistance (-40°C~150°C), etc., and consider the shrinkage rate and mold wear.
Mold Steels: Use corrosion-resistant and highly wear-resistant pre-hardened steels (such as NAK80) or powder metallurgy steels (such as ASP23), and insert cemented carbide in key parts.
Structural Design
Parting Surface: Adopt a multi - section slider structure with a matching accuracy of ±3μm to prevent glue overflow and short circuits.
Ejection System: Implement multi - point balanced ejection, and the diameter of the ejector pins should be adapted to the pitch of the PIN pins.
Cooling System: Employ conformal cooling water channels to ensure uniform cooling of the plastic.
II. Structural Composition
Molding Parts: The upper and lower mold cores form the cavity, determining the shape, size, and surface quality of the product.
Gating System: Composed of the sprue, runners, gates, and cold slug wells, it controls the flow and filling of the plastic.
Guiding Mechanism: Guide pillars and guide bushes ensure accurate alignment of the upper and lower molds during mold closing.
Ejection Mechanism: Ejector pins, push plates, etc. eject the molded product from the cavity.
III. Working Principle
Mold Closing: The injection molding machine drives the mold to close, and the guiding mechanism ensures alignment, followed by the placement of inserts.
Injection Molding: The plastic is heated and melted, then injected into the cavity through the gating system.
Pressure Holding: Maintain pressure to compact and compensate for shrinkage, ensuring the accuracy and quality of the product.
Cooling: The cooling system solidifies the plastic into shape.
Mold Opening and Ejection: The mold opens, and the ejection mechanism ejects the product, completing the cycle.